

Domination is counter-productive it puts a damper on the groups’ best problem solvers.

Presence of some group members, who are powerful and influential may intimidate and prevent other members from participating freely.
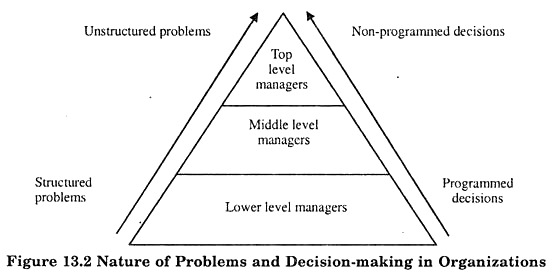
they need to take decisions carefully so that all stakeholders benefit by what they do (Like price the products appropriately, do not resort to unethical practices, do not sell low quality goods etc.) While trying to deliver value to the organisation, managers are expected to keep the interests of all stakeholders also in mind-such as employees, customers, suppliers, the general public etc. These decisions are aimed at furthering the interests of the organisation and can be delegated. Organisational decisions are made by managers, in their official or formal capacity. Personal decisions cannot be delegated and have a limited impact. For example, a personal decision to purchase a Maruti rather than an Ambassador, indirectly helps one firm due to the sale and hurts another because of the lost sale. They affect the organisation, in an indirect way. Such decisions, pertain to managers as individuals. Personal and Organizational Decisions:ĭecisions to watch television, to study, or retire early are examples of personal decisions. The decisions taken by managers at various points of time may be classified thus:ġ. Both are based on forecasts and assumptions about future risk and uncertainty. Both involve choice among alternative courses of action. Both are intellectual processes, demanding discretion and judgment. Depending on the situational requirements, managers take suitable decisions using discretion and judgment.Īs Koontz indicated, ‘decision making is the core of planning’. A manager for example, may hire people based on merit regularly and also pick up candidates recommended by an influential party, at times. Moreover, it is a process concerned with ‘identifying worthwhile things to do’ in a dynamic setting. It is a process of using inputs effectively in the solution of selected problems and the creation of outputs that have utility. Decision implies freedom to the decision maker regarding the final choice it is uniquely human and is the product of deliberation, evaluation and thought.ĭecision-making is characterized as a process, rather than as, one static entity. Many decisions are based on emotions or instincts. Decision-making cannot be completely quantified nor is it based mainly on reason or intuition. Part of it can be learned, but part of it depends upon the personal characteristics of the decision maker. It has both the intuitive and deductive logic it contains conscious and unconscious aspects. A decision represents a course of behavior chosen from a number of possible alternatives”.Īccording to Haynes and Massie, “a decision is a course of action which is consciously chosen for achieving a desired result”.ĭecision-making is not a purely intellectual process. McFarland, “A decision is an act of choice – wherein an executive forms a conclusion about what must not be done in a given situation. This indicates that managers must necessarily develop decision making skills.Īccording to D. So, the quality of managers’ decisions is the Yardstick of their effectiveness and value to the organization. Whether the problem is large or small in the organization, it is usually the manager who has to comfort it and decide what action to take. To decide means to cut off on to come to a conclusion. It is a made to achieve goals in the organization. Hence, in organization an execute forms a conclusion by developing various course of actions in a given situation. It means decision comes in picture when various alternatives are present. As per his opinion a post of position cannot be said to be managerial until and unless the right of Decision-Making is attached to it.Ī decision is a course of action which is consciously chosen from among a set of alternatives to achieve a desired result. It is because of its perverseness of Decision-Making that professor Herbert Simons has said the process of managing as a process of decision-making. Each managerial decision, whether it is concerned with planning, organizing, staffing or directing is concerned with the process of decision-making. Success or failure of an organization mainly depends upon the quality of decision that the managers take at all levels. One of the most important functions of a manager is to take decisions in the organization. Meaning and Definitions of Decision Making:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
